Lung Cancer Prevention (PDQ®): Prevention - Patient Information [NCI]
This information is produced and provided by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The information in this topic may have changed since it was written. For the most current information, contact the National Cancer Institute via the Internet web site at http://cancer.gov or call 1-800-4-CANCER.
What Is Prevention?
Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. By preventing cancer, the number of new cases of cancer in a group or population is lowered. Hopefully, this will lower the number of deaths caused by cancer.
To prevent new cancers from starting, scientists look at risk factors and protective factors. Anything that increases your chance of developing cancer is called a cancer risk factor; anything that decreases your chance of developing cancer is called a cancer protective factor.
Some risk factors for cancer can be avoided, but many cannot. For example, both smoking and inheriting certain genes are risk factors for some types of cancer, but only smoking can be avoided. Regular exercise and a healthy diet may be protective factors for some types of cancer. Avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors may lower your risk, but it does not mean that you will not get cancer.
Different ways to prevent cancer are being studied, including:
- changing lifestyle or eating habits
- avoiding things known to cause cancer
- taking medicines to treat a precancerous condition or to keep cancer from starting
General Information About Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the body as you breathe in. They release carbon dioxide, a waste product of the body's cells, as you breathe out. Each lung has sections called lobes. The left lung has two lobes. The right lung is slightly larger, and has three lobes. A thin membrane called the pleura surrounds the lungs. Two tubes called bronchi lead from the trachea (windpipe) to the right and left lungs. The bronchi are sometimes also involved in lung cancer. Tiny air sacs called alveoli and small tubes called bronchioles make up the inside of the lungs. 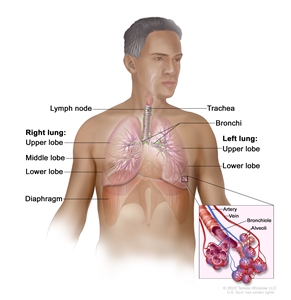
Anatomy of the respiratory system showing the trachea, the right and left lungs and their lobes, and the bronchi. The lymph nodes and the diaphragm are also shown. Oxygen is inhaled into the lungs and passes through the alveoli (the tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles) and into the bloodstream (see inset), where it travels to the tissues throughout the body.
There are two main types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Other PDQ summaries containing information related to lung cancer include:
- Lung Cancer Screening
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
- Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
- Cigarette Smoking: Health Risks and How to Quit
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women.
Lung cancer rates and deaths are higher in Black men than in other racial and ethnic group in the United States.
Lung Cancer Prevention
Avoiding risk factors and increasing protective factors may help prevent lung cancer.
Avoiding cancer risk factors may help prevent certain cancers. Risk factors include smoking, having overweight, and not getting enough exercise. Increasing protective factors such as quitting smoking and exercising may also help prevent some cancers. Talk to your doctor or other health care professional about how you might lower your risk of cancer.
The following are risk factors for lung cancer:
Cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking
Tobacco smoking is the most important risk factor for lung cancer. Cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking all increase the risk of lung cancer. Tobacco smoking causes about 9 out of 10 cases of lung cancer in men and about 8 out of 10 cases of lung cancer in women.
Studies have shown that smoking low tar or low nicotine cigarettes does not lower the risk of lung cancer.
Studies also show that the risk of lung cancer from smoking cigarettes increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the number of years smoked. People who smoke have about 20 times the risk of lung cancer compared to those who do not smoke.
Secondhand smoke
Being exposed to secondhand tobacco smoke is also a risk factor for lung cancer. Secondhand smoke is the smoke that comes from a burning cigarette or other tobacco product, or that is exhaled by smokers. People who inhale secondhand smoke are exposed to the same cancer-causing agents as smokers, although in smaller amounts. Inhaling secondhand smoke is called involuntary or passive smoking.
Family history
Having a family history of lung cancer is a risk factor for lung cancer. People with a relative who has had lung cancer may be twice as likely to have lung cancer as people who do not have a relative who has had lung cancer. Because cigarette smoking tends to run in families and family members are exposed to secondhand smoke, it is hard to know whether the increased risk of lung cancer is from the family history of lung cancer or from being exposed to cigarette smoke.
HIV infection
Being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the cause of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), is linked with a higher risk of lung cancer. People infected with HIV may have more than twice the risk of lung cancer than those who are not infected. Since smoking rates are higher in those infected with HIV than in those not infected, it is not clear whether the increased risk of lung cancer is from HIV infection or from being exposed to cigarette smoke.
Environmental risk factors
- Radiation exposure: Being exposed to radiation is a risk factor for lung cancer. Atomic bomb radiation, radiation therapy, imaging tests, and radon are sources of radiation exposure:
- Atomic bomb radiation: Being exposed to radiation after an atomic bomb explosion increases the risk of lung cancer.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy to the chest may be used to treat certain cancers, including breast cancer and Hodgkin lymphoma. Radiation therapy uses x-rays, gamma rays, or other types of radiation that may increase the risk of lung cancer. The higher the dose of radiation received, the higher the risk. The risk of lung cancer following radiation therapy is higher in patients who smoke than in nonsmokers.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as CT scans, expose patients to radiation. Low-dose spiral CT scans expose patients to less radiation than higher dose CT scans. In lung cancer screening, the use of low-dose spiral CT scans can lessen the harmful effects of radiation.
- Radon: Radon is a radioactive gas that comes from the breakdown of uranium in rocks and soil. It seeps up through the ground, and leaks into the air or water supply. Radon can enter homes through cracks in floors, walls, or the foundation, and levels of radon can build up over time.
Studies show that high levels of radon gas inside the home or workplace increase the number of new cases of lung cancer and the number of deaths caused by lung cancer. The risk of lung cancer is higher in smokers exposed to radon than in nonsmokers who are exposed to it. In people who have never smoked, about 26% of deaths caused by lung cancer have been linked to being exposed to radon.
- Workplace exposure: Studies show that being exposed to the following substances increases the risk of lung cancer:
- asbestos
- arsenic
- chromium
- nickel
- beryllium
- cadmium
- tar and soot
These substances can cause lung cancer in people who are exposed to them in the workplace and have never smoked. As the level of exposure to these substances increases, the risk of lung cancer also increases. The risk of lung cancer is even higher in people who are exposed and also smoke.
- Air pollution: Studies show that living in areas with higher levels of air pollution increases the risk of lung cancer.
Beta carotene supplements in heavy smokers
Taking beta carotene supplements (pills) increases the risk of lung cancer, especially in smokers who smoke one or more packs a day. The risk is higher in smokers who have at least one alcoholic drink every day.
The following are protective factors for lung cancer:
Not smoking
The best way to prevent lung cancer is to not smoke.
Quitting smoking
Smokers can decrease their risk of lung cancer by quitting. In smokers who have been treated for lung cancer, quitting smoking lowers the risk of new lung cancers. Counseling, the use of nicotine replacement products, and antidepressant therapy have helped smokers quit for good.
In a person who has quit smoking, the chance of preventing lung cancer depends on how many years and how much the person smoked and the length of time since quitting. After a person has quit smoking for 10 years, the risk of lung cancer decreases 30% to 60%.
Although the risk of dying from lung cancer can be greatly decreased by quitting smoking for a long period of time, the risk will never be as low as the risk in nonsmokers. This is why it is important for young people not to start smoking.
See the following for more information on quitting smoking:
- Tobacco (includes help with quitting)
- Cigarette Smoking: Health Risks and How to Quit
Lower exposure to workplace risk factors
Laws that protect workers from being exposed to cancer-causing substances, such as asbestos, arsenic, nickel, and chromium, may help lower their risk of developing lung cancer. Laws that prevent smoking in the workplace help lower the risk of lung cancer caused by secondhand smoke.
Lower exposure to radon
Lowering radon levels may lower the risk of lung cancer, especially among cigarette smokers. High levels of radon in homes may be reduced by taking steps to prevent radon leakage, such as sealing basements.
It is not clear if the following decrease the risk of lung cancer:
Diet
Some studies show that people who eat high amounts of fruits or vegetables have a lower risk of lung cancer than those who eat low amounts. However, since smokers tend to have less healthy diets than nonsmokers, it is hard to know whether the decreased risk is from having a healthy diet or from not smoking.
Physical activity
Some studies show that people who are physically active have a lower risk of lung cancer than people who are not. However, since smokers tend to have different levels of physical activity than nonsmokers, it is hard to know if physical activity affects the risk of lung cancer.
The following do not decrease the risk of lung cancer:
Beta carotene supplements in nonsmokers
Studies of nonsmokers show that taking beta carotene supplements does not lower their risk of lung cancer.
Vitamin E supplements
Studies show that taking vitamin E supplements does not affect the risk of lung cancer.
Cancer prevention clinical trials are used to study ways to prevent cancer.
Cancer prevention clinical trials are used to study ways to lower the risk of developing certain types of cancer. Some cancer prevention trials are conducted with healthy people who have not had cancer but who have an increased risk for cancer. Other prevention trials are conducted with people who have had cancer and are trying to prevent another cancer of the same type or to lower their chance of developing a new type of cancer. Other trials are done with healthy volunteers who are not known to have any risk factors for cancer.
The purpose of some cancer prevention clinical trials is to find out whether actions people take can prevent cancer. These may include eating fruits and vegetables, exercising, quitting smoking, or taking certain medicines, vitamins, minerals, or food supplements.
New ways to prevent lung cancer are being studied in clinical trials.
Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCI's clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government's center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about lung cancer prevention. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Screening and Prevention Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Screening and Prevention Editorial Board. PDQ Lung Cancer Prevention. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/patient/lung-prevention-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389497]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website's E-mail Us.
Last Revised: 2024-07-26
If you want to know more about cancer and how it is treated, or if you wish to know about clinical trials for your type of cancer, you can call the NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-422-6237, toll free. A trained information specialist can talk with you and answer your questions.


